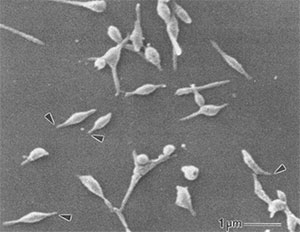
Signs and symptoms
In general, infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Recombinants are mild. Once someone is infected with the bacteria, symptoms usually appear after 1 to 4 weeks. Symptoms depend on the type of infection. The most common type of infection is tracheobronchitis (chest cold), but pneumonia (lung infection) can occur.
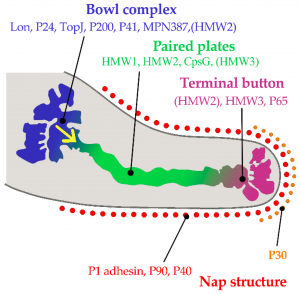
Common symptoms of a chest cold include:
- Throat pain
- Feeling tired
- Fever
- Cough that gets worse slowly and can last for weeks or months
- Headache
Common symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough that can produce mucus
- Fever and chills
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest pain
- Feeling tired
Children under 5 years of age may have different symptoms than older children and may have the following cold-like symptoms:
- sneezing
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Throat pain
- Crying eyes
- wheezing
- vomiting
- Diarrhoea
Treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the first line of treatment for MP. Children receive different antibiotics than adults to prevent potentially dangerous side effects. Macrolides, the first choice of antibiotics for children, include:
- erythromycin
- clarithromycin
- roxithromycin
- azithromycin
Antibiotics prescribed for adults include:
- doxycycline
- tetracycline
- quinolones, such as levofloxacin and moxifloxacin
Corticosteroids
Sometimes antibiotics alone are not enough and you need to be treated with corticosteroids to control the inflammation. Examples of such corticosteroids include:
- prednisolone
- methylprednisolone
Immunomodulatory therapy
If you have severe MP, you may need other “immunomodulatory therapy” in addition to corticosteroids, including intravenous immunoglobulin, or IVIG.
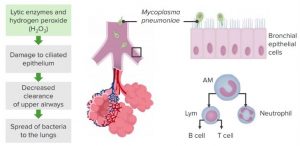
Diagnosis of mycoplasma pneumonia
PM usually develops without noticeable symptoms during the first 1 to 3 weeks after exposure. Early diagnosis is difficult because the body does not instantly reveal an infection. The infection can manifest outside your lung. If this happens, signs of infection may include ruptured red blood cells, a skin rash, and joint involvement. To make a diagnosis, your doctor uses a Trusted Source stethoscope to listen for any abnormal sounds in your breathing. A chest X-ray and CT scan can also help your doctor make a diagnosis.
Prevention of mycoplasma pneumonia
The risk of contracting MP peaks in the fall and winter months. Closed or crowded places make it easier for the infection to spread from person to person. To reduce the risk of infection, try the following:
- Sleep 6 to 8 hours a night.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Avoid people with symptoms of PM.
- Practice good hygiene by washing your hands before eating or after interacting with infected people.